In Chapter is described how the Tolkowsky Round works. And what will happen if we will decrease or increase diamond Pavilion angle.
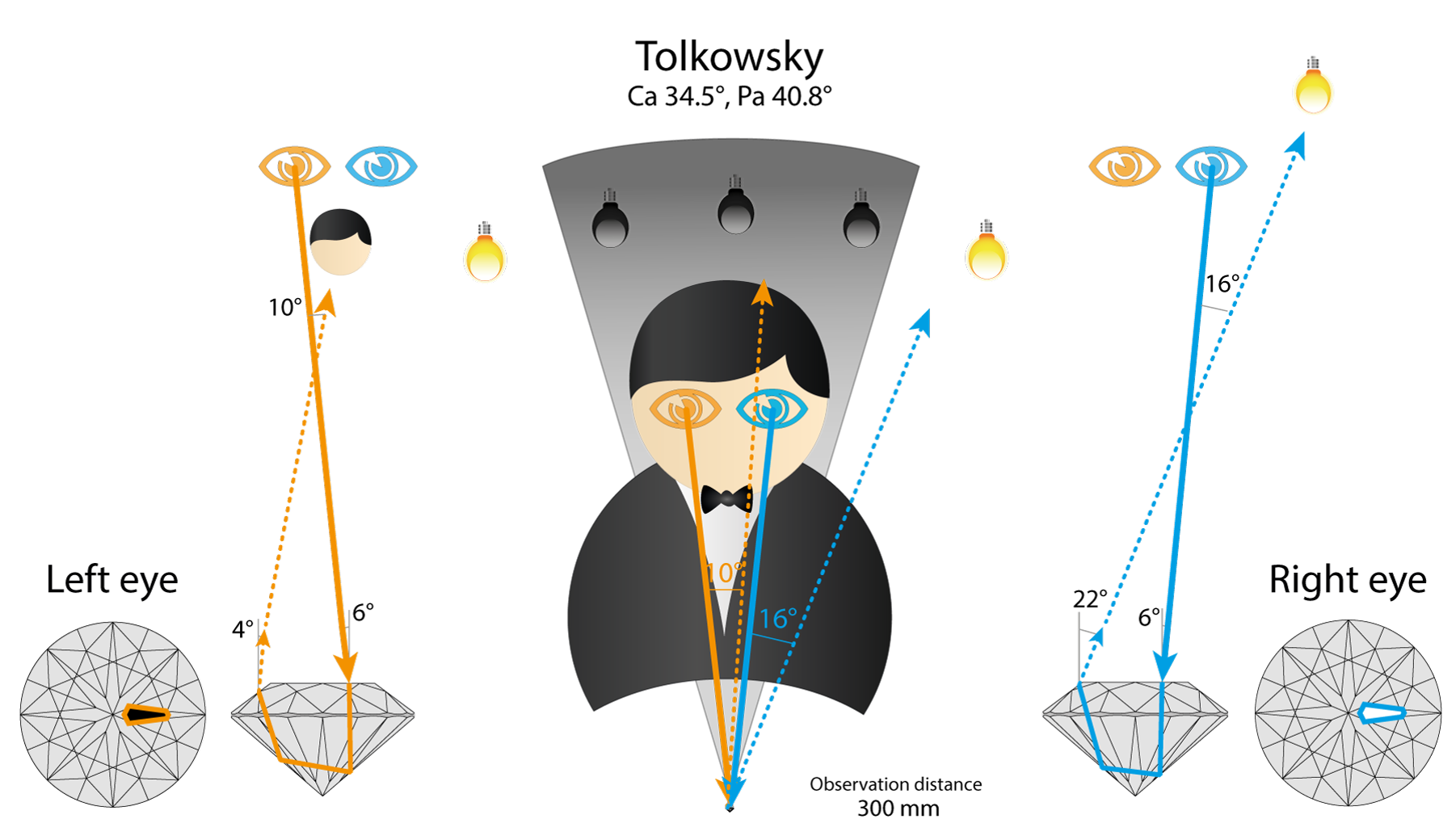
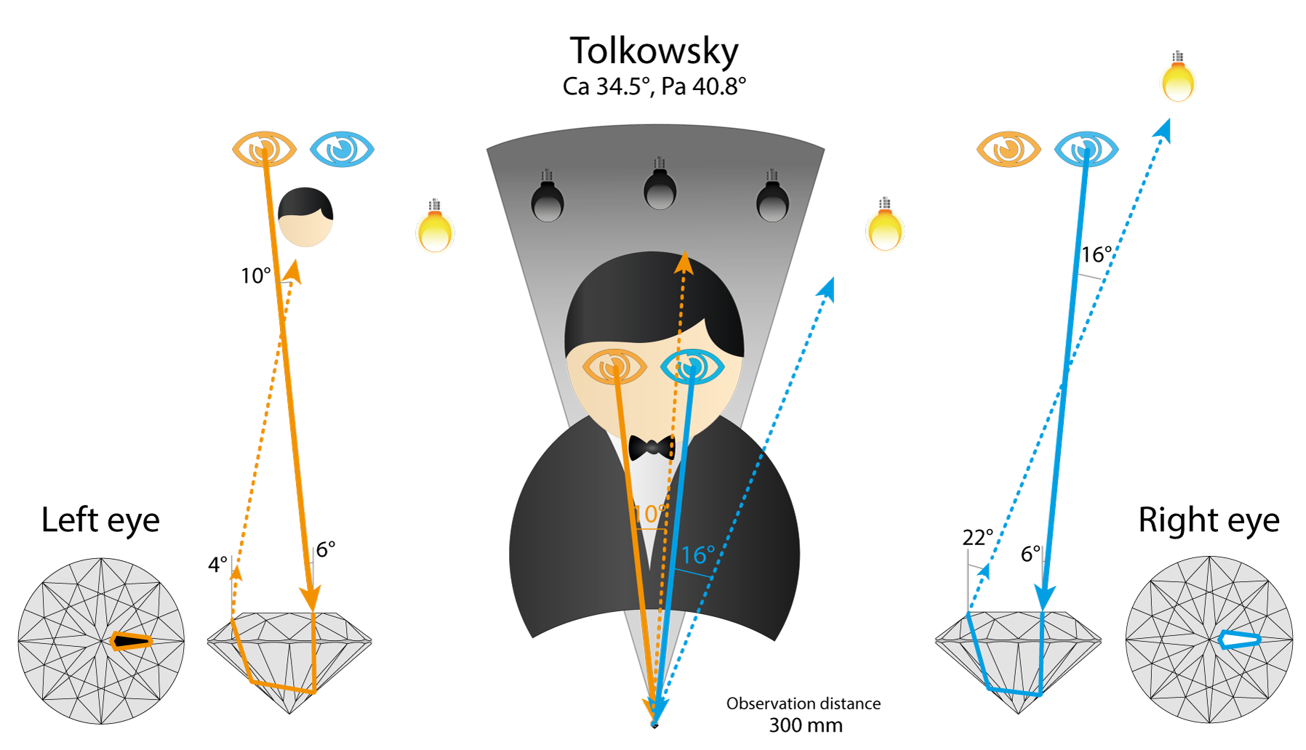
Let’s consider optical theory for arrow facet under the table. Right eye see white flash reflected from the light source on the right.
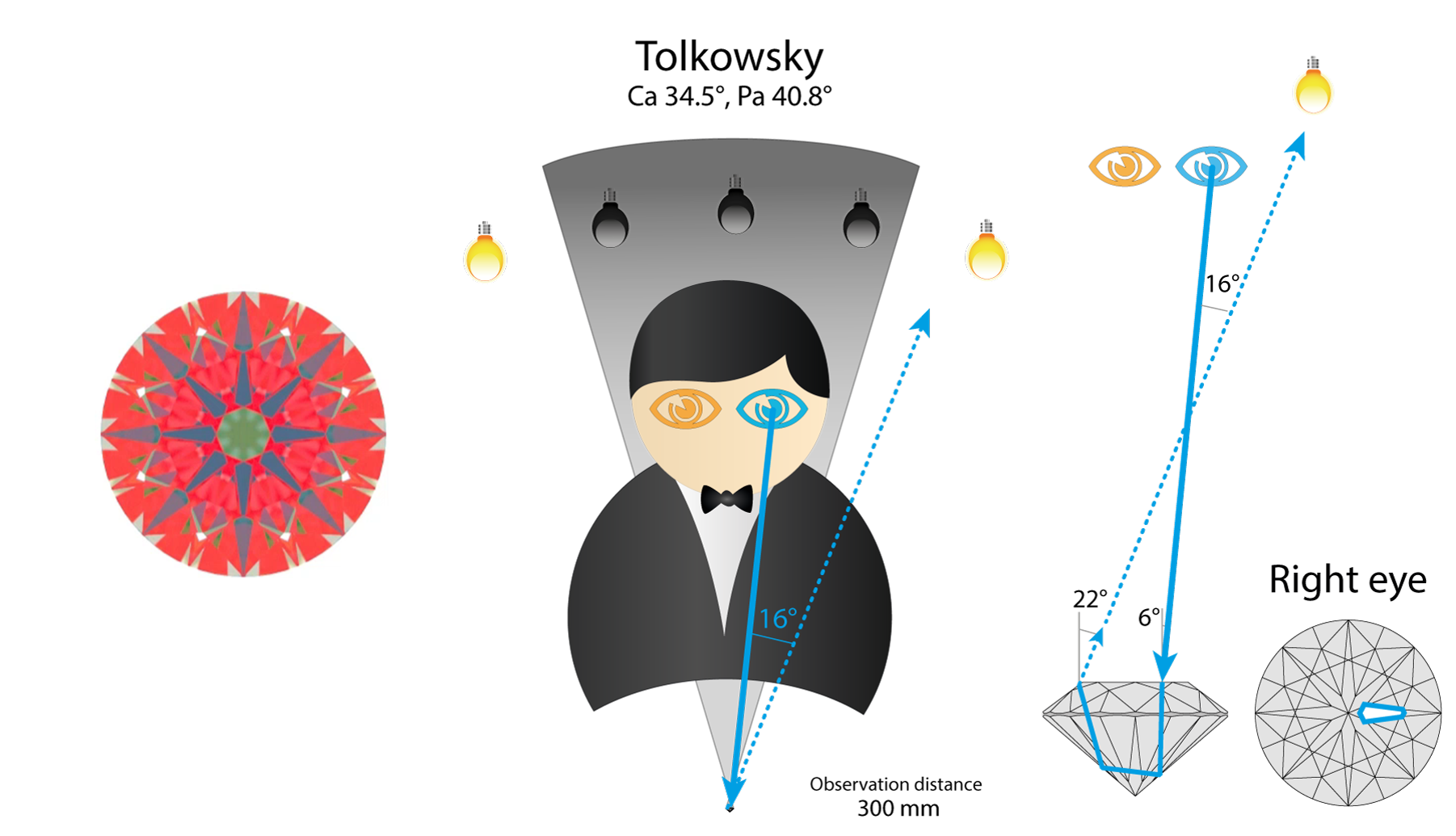
The same area is black for left eye, because it see the observer’s head reflection.
So in one area of space our eyes see very different and contradictory images:
- — white light source reflection flash
- — and black head reflection.
Difference in signal intensity is more than 1000 times.
How Round Diamond Cut works?
We described how the Tolkowsky Round works. Let’s check now Rounds with different proportions. What will happen if we will decrease or increase Pavilion angle.
Tolkowsky
Ca 34.5, Pa 40.8
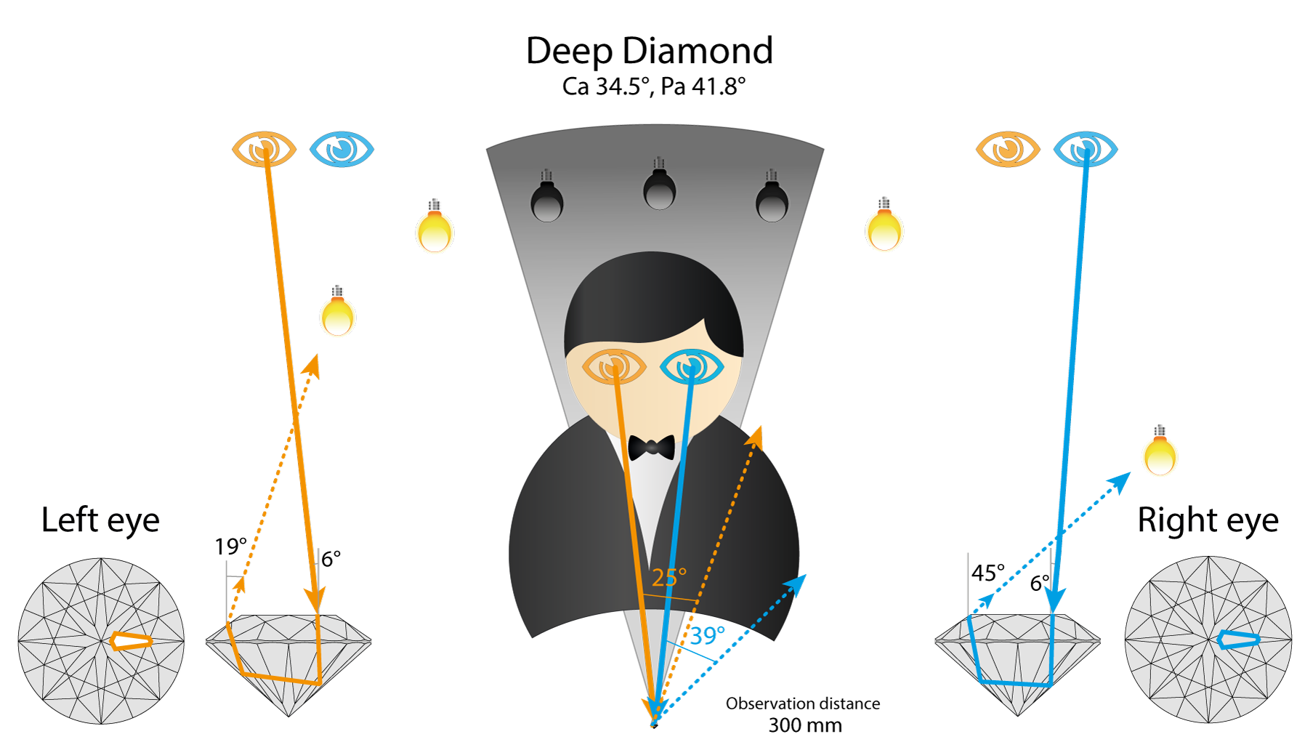
We will check two shallower stones. One with Pa 39.6 and another very shallow. And two deeper stones: one with Pa 41.6, and another very deep “Nail Head” diamond.
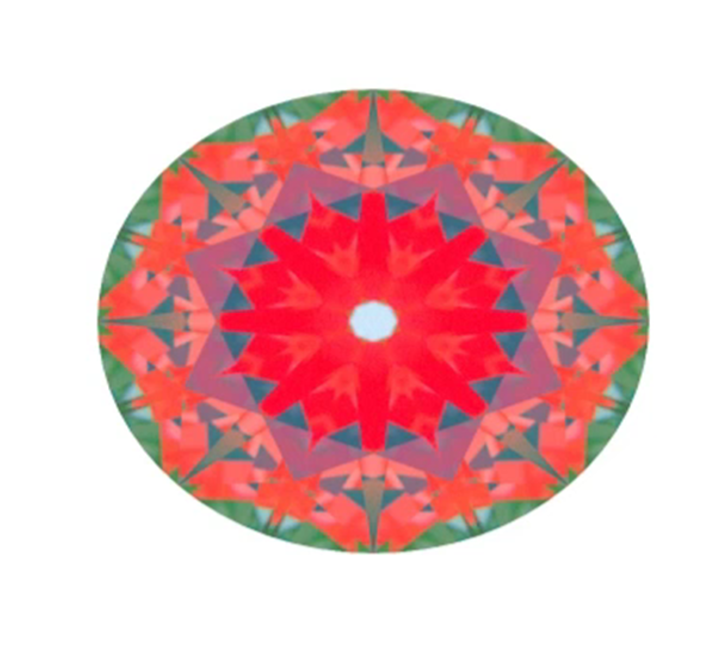
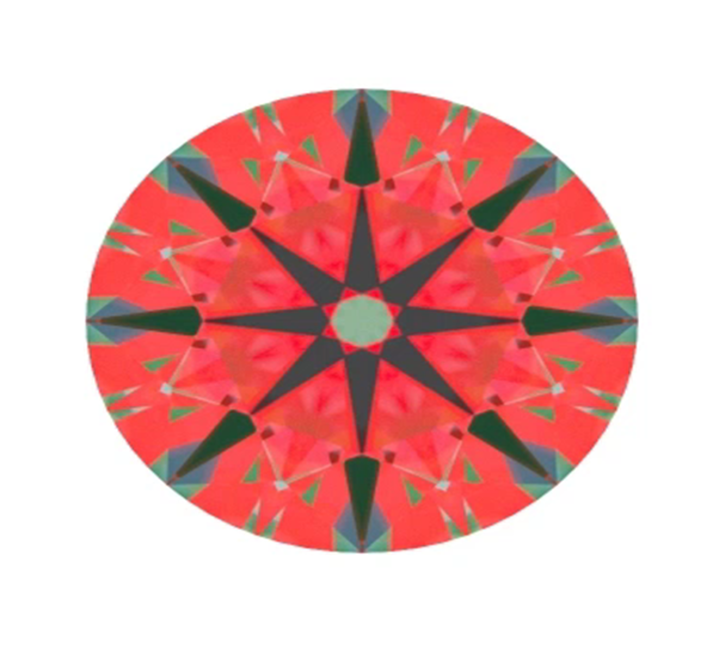
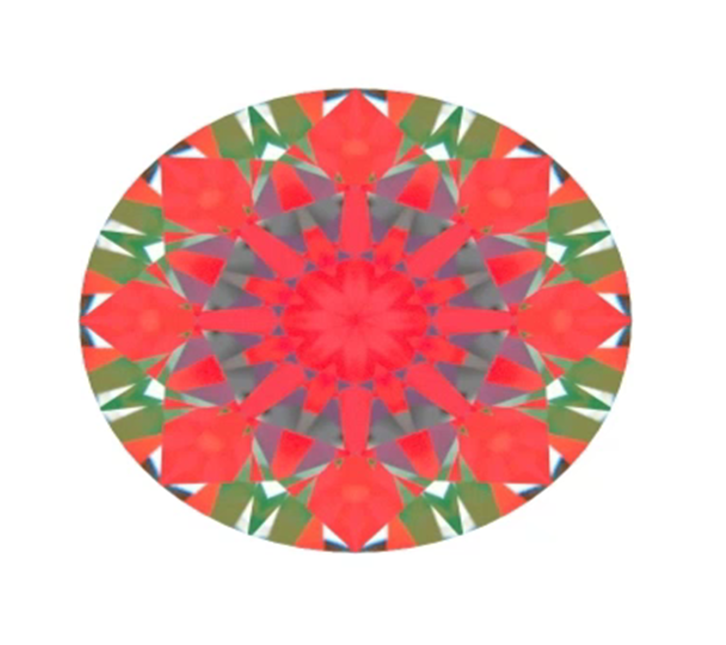
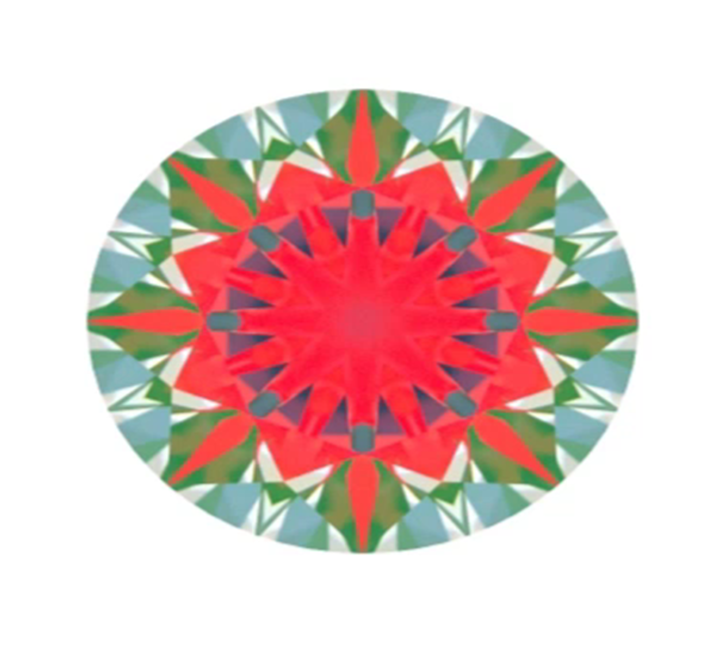





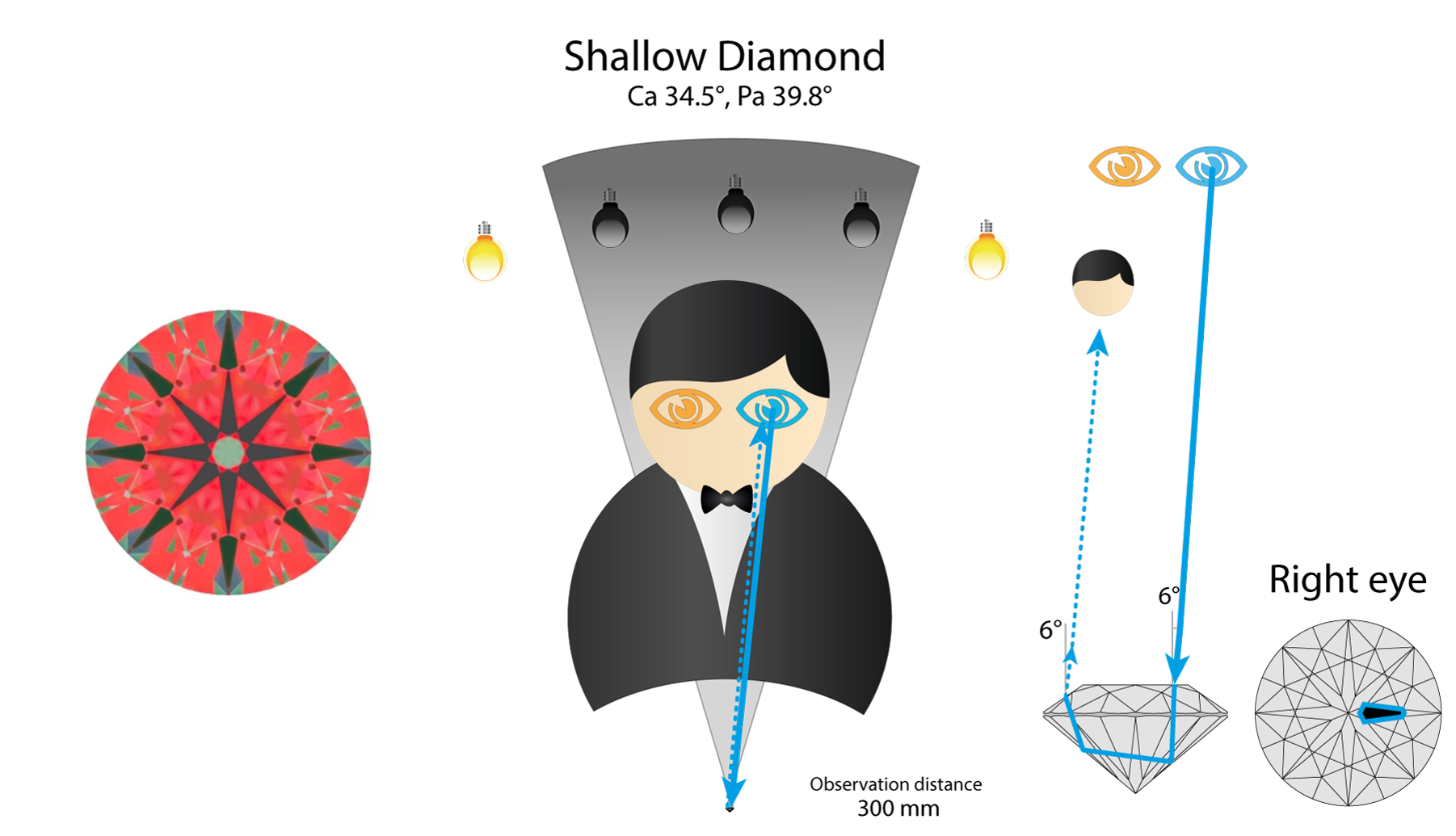
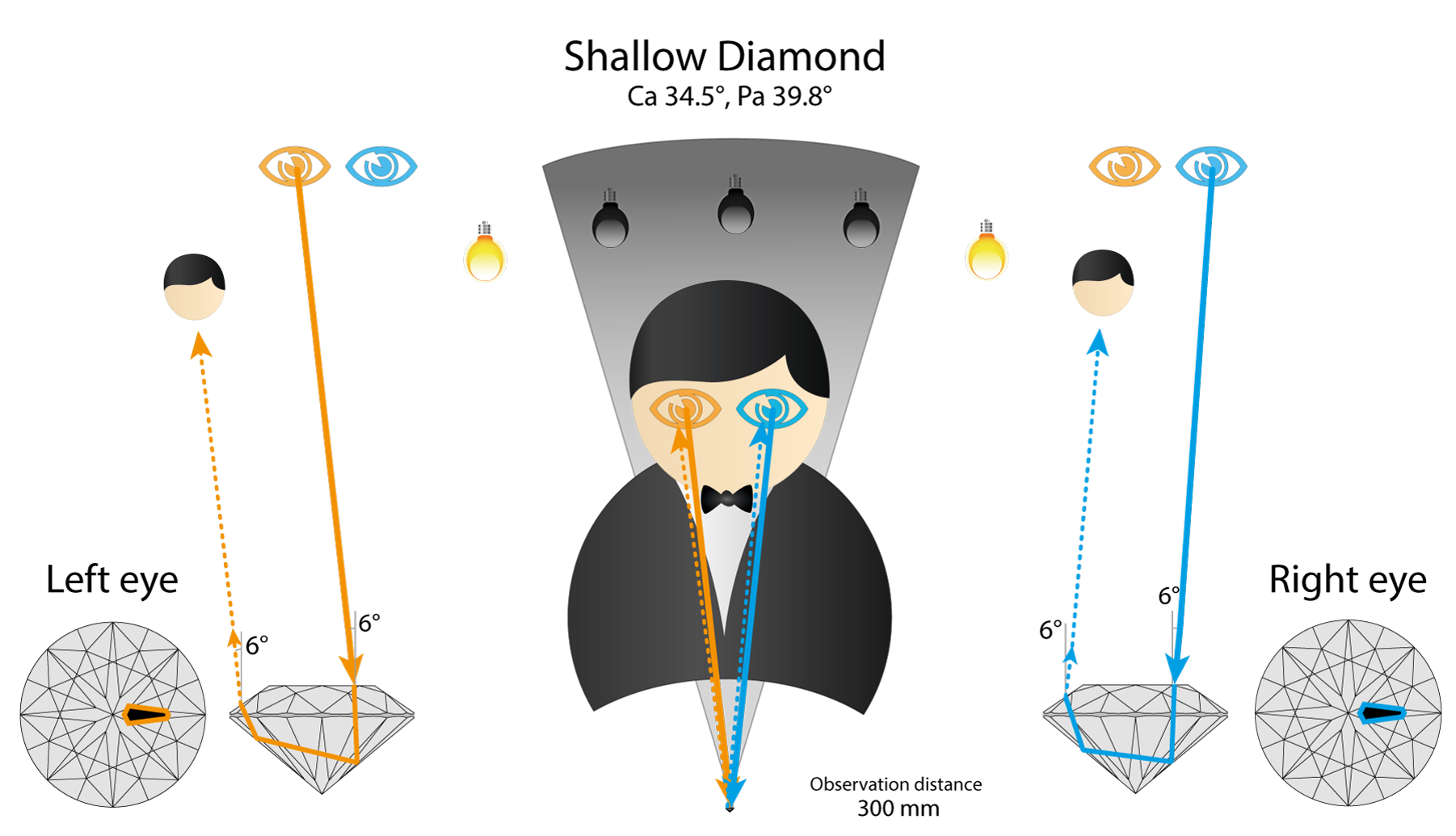
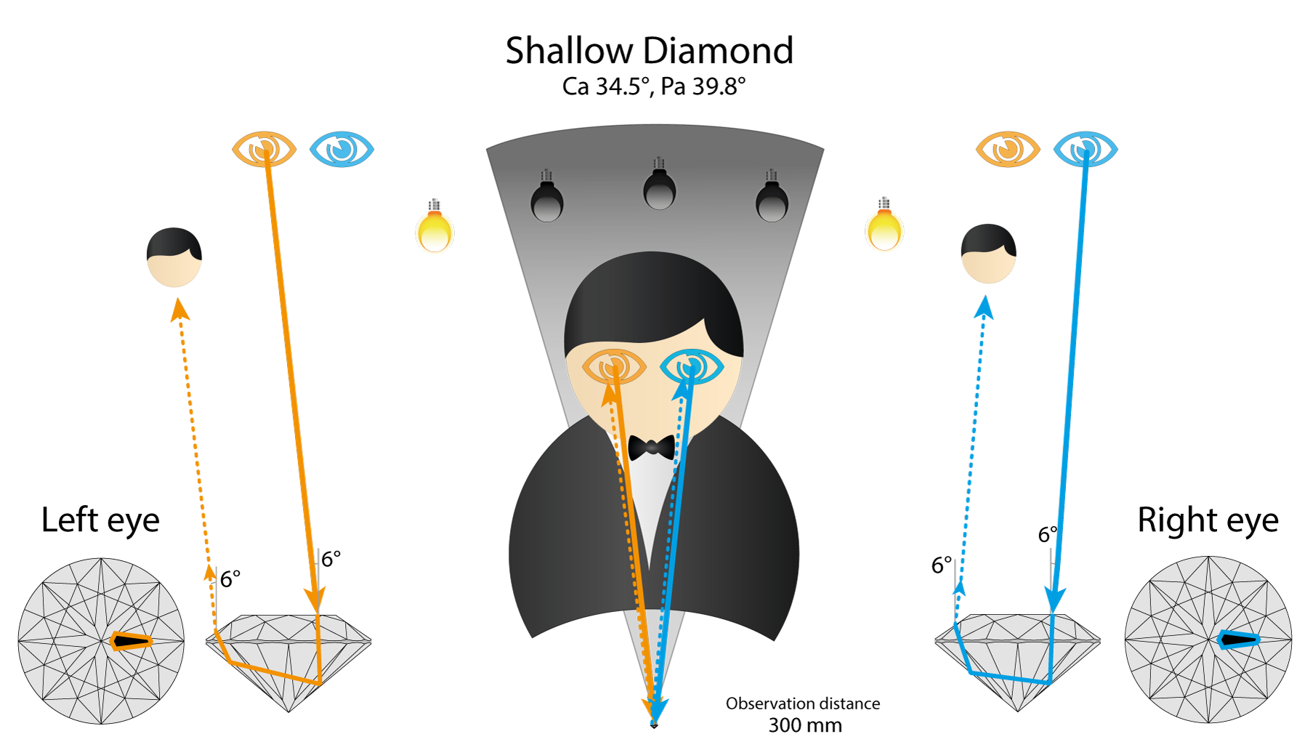
Now let’s check shallow diamond. It returns the ray from Right eye directly to the observer head. So marked arrow is black.
Left eye also see black, because of observer’s body reflection. So both eyes see black and reflects observer head. This is worst case scenario. Arrows in such stone in completely black (because there is no chance to have a light source in observer’s head area).
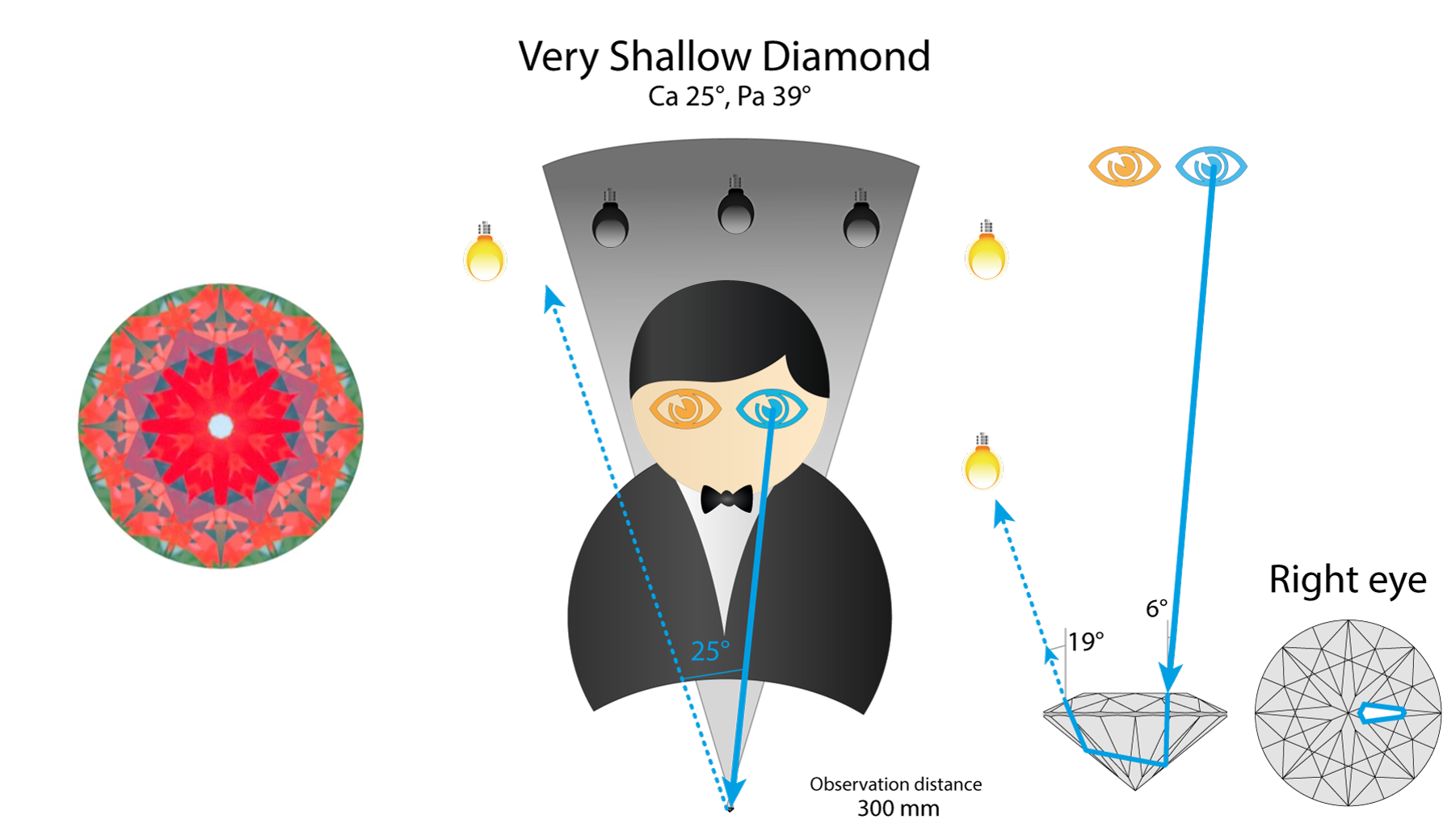
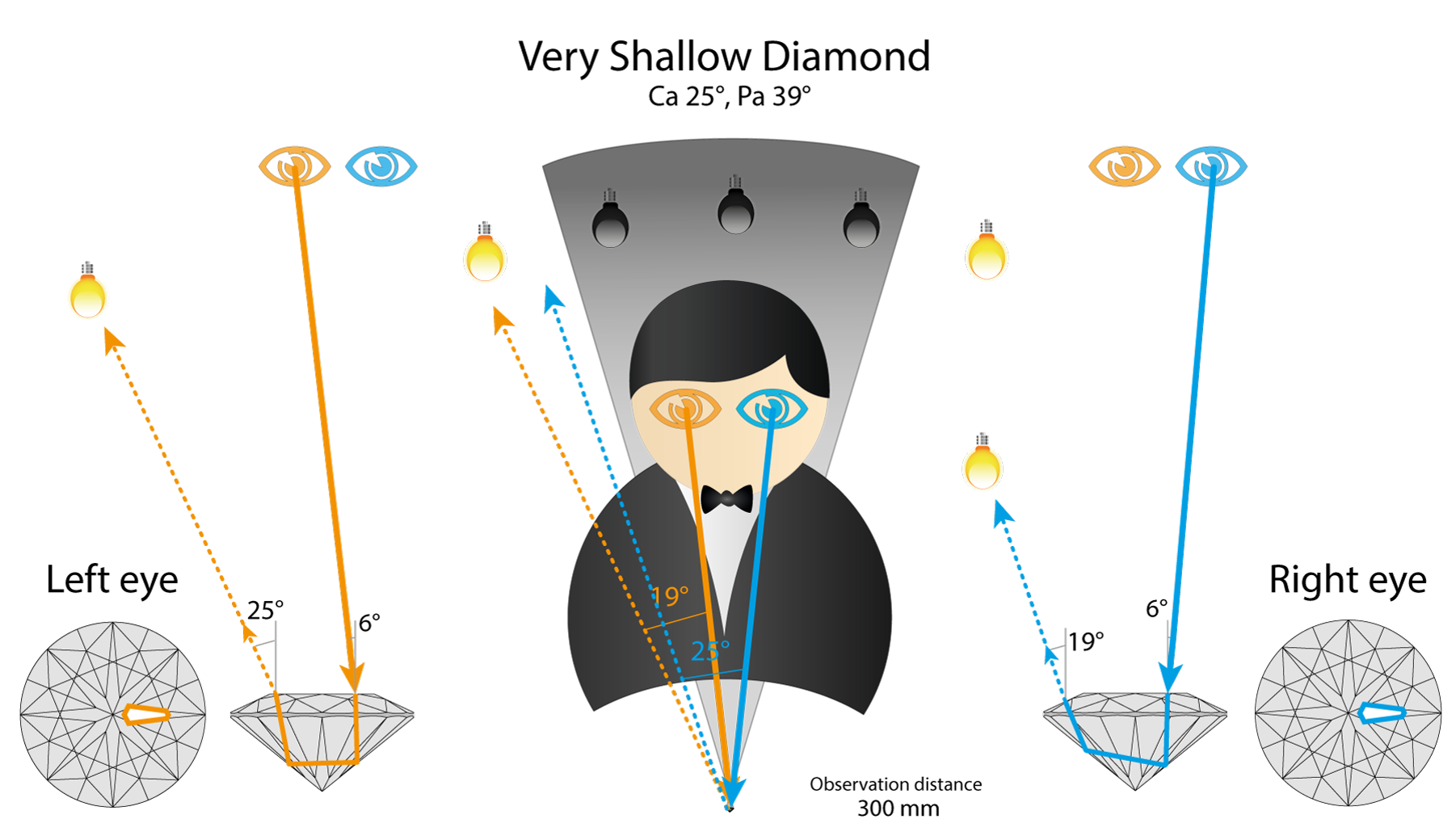
Very shallow stone show different ray path. It will reflect light source that on the left side of observer (note that it is different from Tolkowsky).
And for left eye also we see light source that is on the left side of the observer. In very shallow diamond selected facet is white in both eyes. So the diamond has high objective brightness. But it lacks contrast, and thus loses in Brilliance.
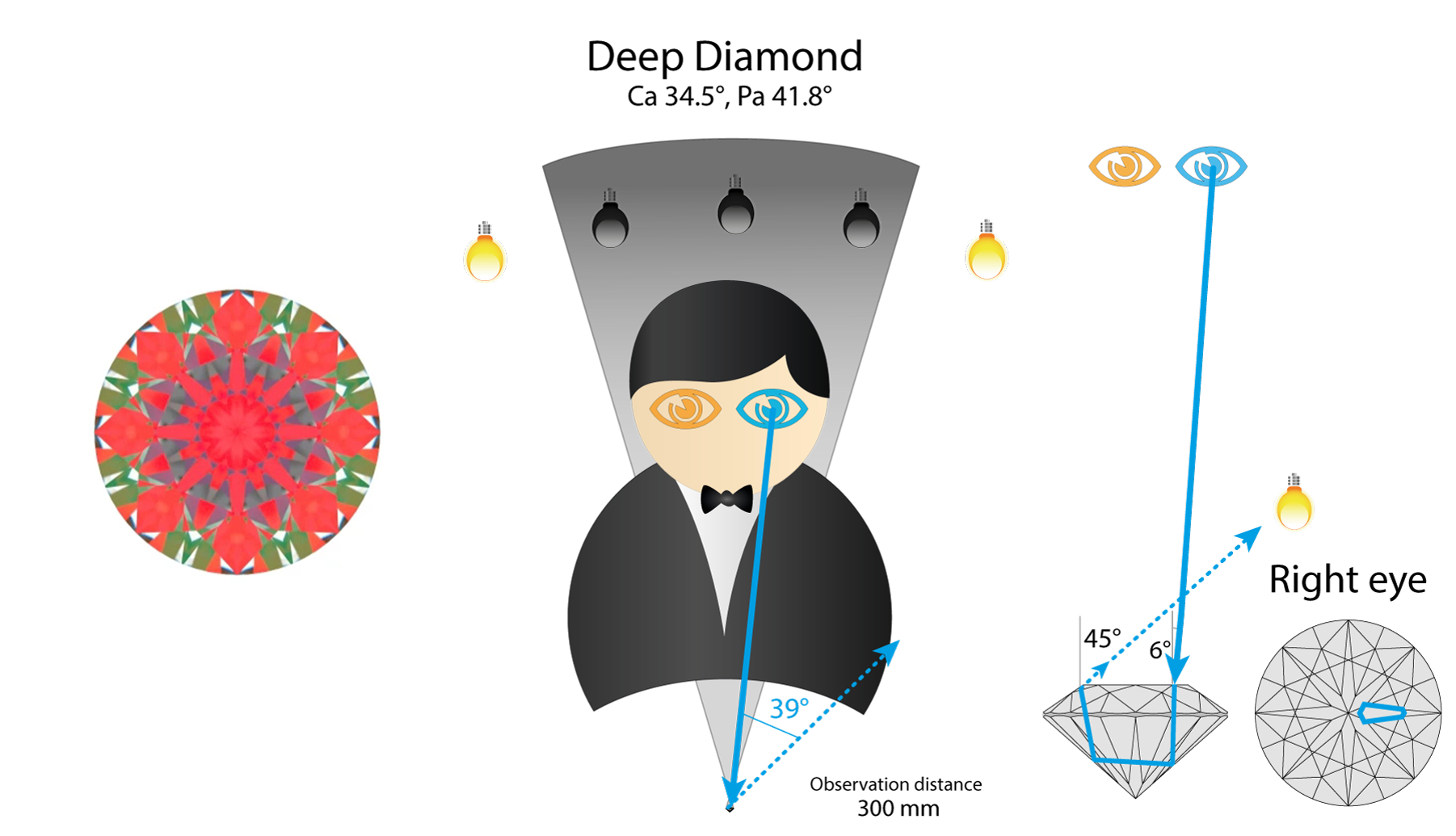
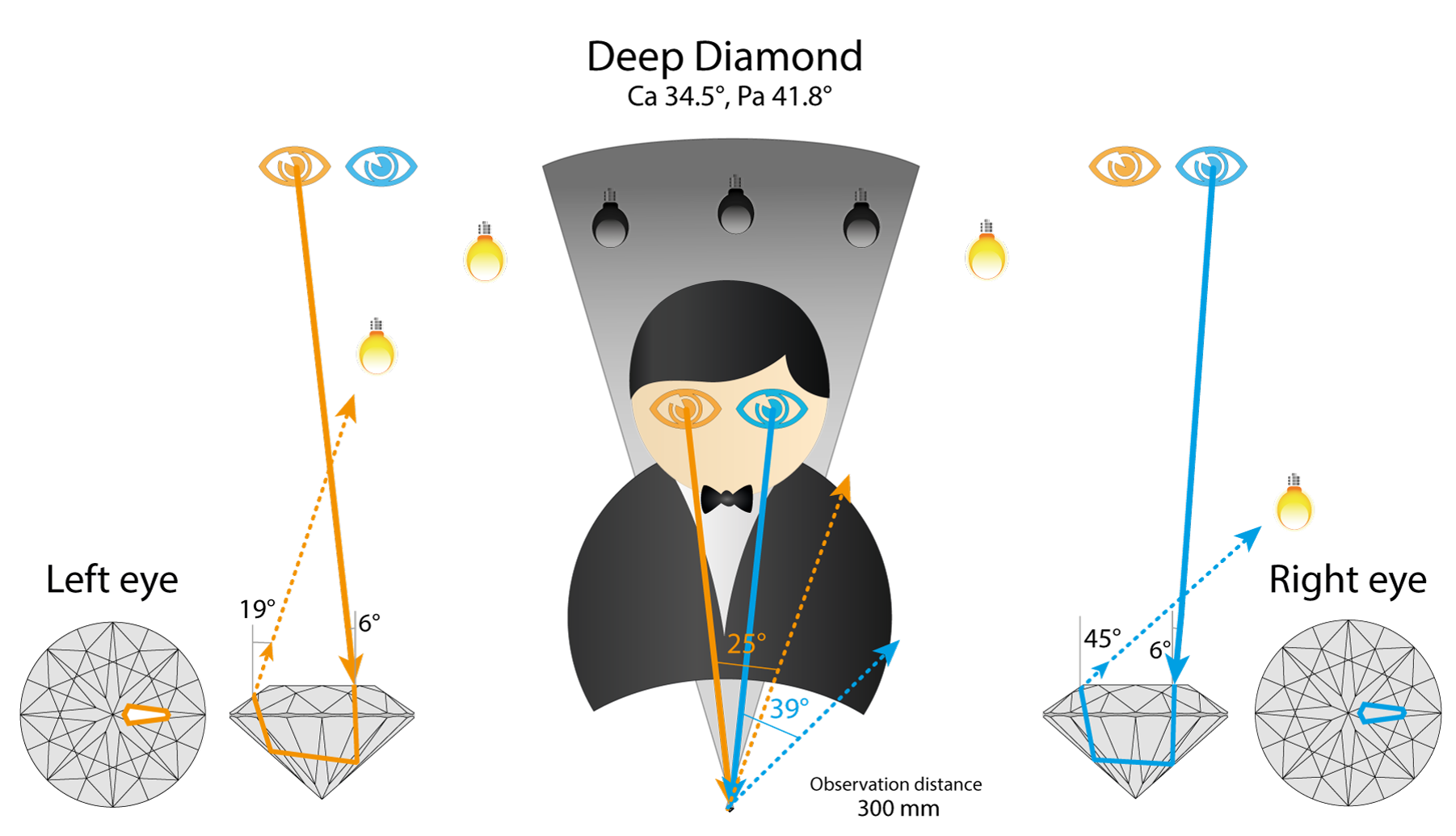
Deep diamond will act close to Tolkowsky, but will reflect Light source from much steeper angle
So deep diamond has selected facet white in both eyes. We already considered this case earlier.
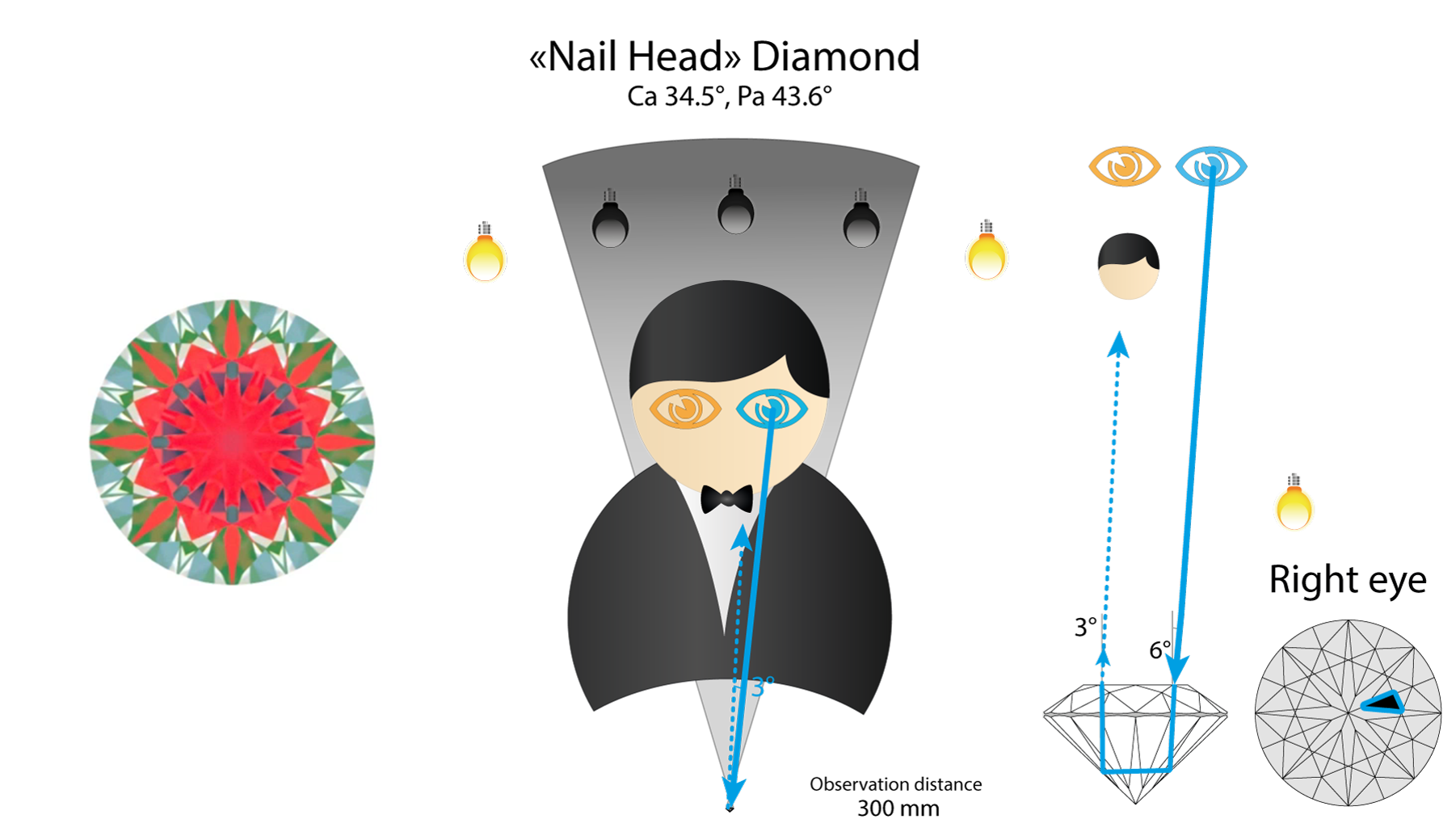
“Nail head” stone will give full internal reflection and redirect light to the observer head.
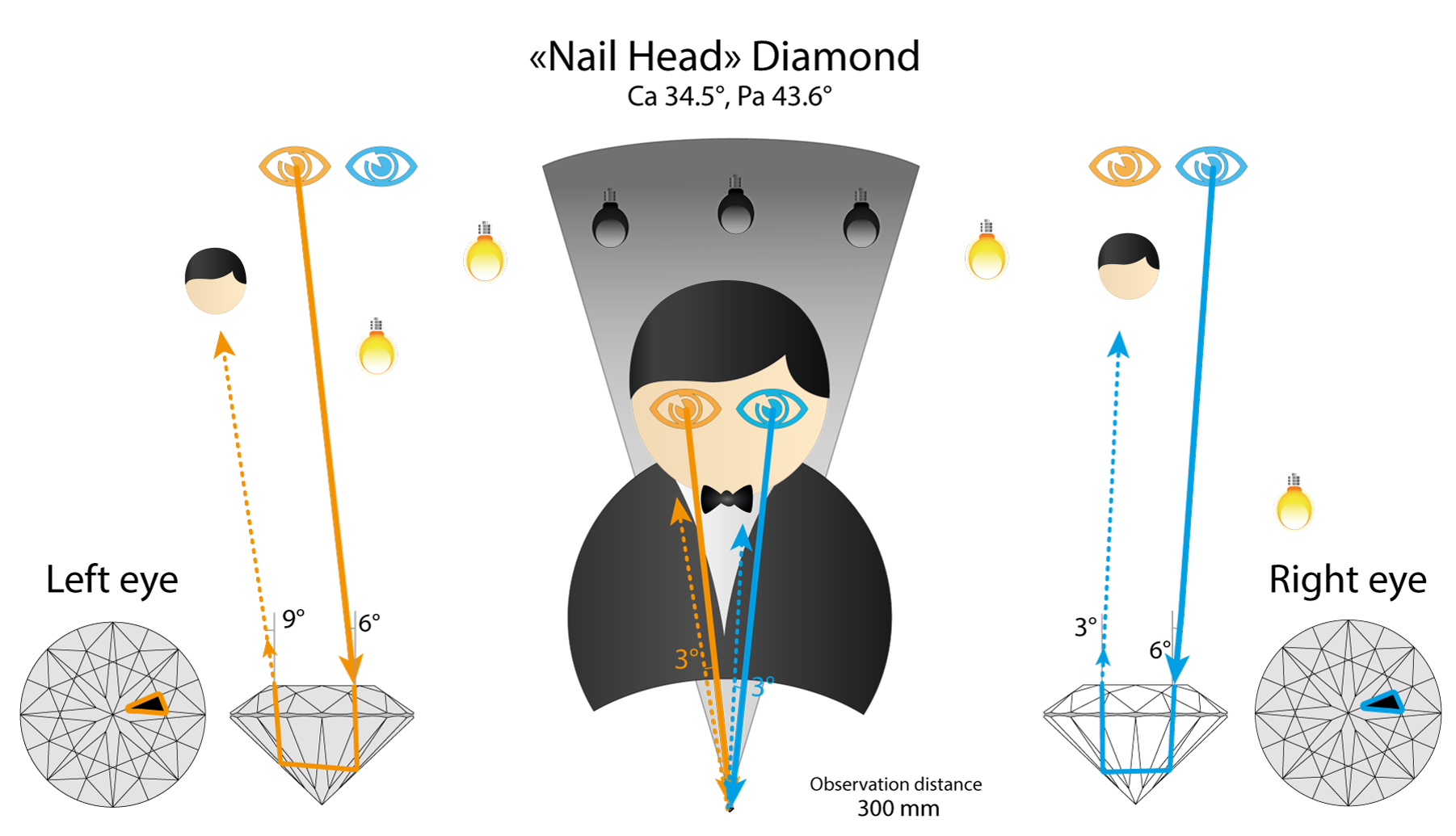
Let’s summarize what we have found. If we change Pa from Tolkowsky then we reduce Binocular rivalry of the Round cut. (Pa 39.8 both eyes see black, Pa 41.8 both eyes see white).
Diamonds Tilt 10º ± 5º From Face-up Position
Another very important feature – is the Facet Speed during the diamond tilting related with Temporal contrast.
When consumer rocks the diamond during the observation – the ray path for facets changes as we can see on the video. Diamond scans the surrounding space and reflects light sources to the observer.
In this demonstration we tilt diamond by 10 degrees. Very shallow diamond and “Nail head” reflects the same area in space during this rotation. It means that these stones reflection of observer’s head is very stable. And even during rotation they will remain black creating ”Dead zones” effect (areas in diamond that always remain black). This results very bad performance of these stones.
Shallow diamond change ray path angle by 1.7 degrees. Tolkowsky displays 4.3 degrees ray angle variation. And Deep stone has highest value among selected stones.
Generally high flash speed during the stone rotation is positive as it allows diamond to produce flashes more often.

